 Profiles of Venezuela Import and Export Data
Profiles of Venezuela Import and Export Data
Venezuela Import and Export Data is also called Venezuela Import Export Data, or Venezuela Import and Export Trade Data, Venezuela Trade Data. There are 2 kinds of Venezuela Import and Export Data: Venezuela customs Data (VECD) and Venezuela Statistics Data(VESD).
 Profiles of Venezuela Customs Data (VECD)
Profiles of Venezuela Customs Data (VECD)
Venezuela customs Data (VECD) is also called Venezuela Customs Import and Export Data, or Venezuela Customs Import and Export Data with company, Venezuela Customs Data with company. VECD is provided according to the-first-6- digit HS Code. We provide actual live VECD since 2000 onwards.
Venezuela customs import Data cover ImpExp, 10-digit HS Code, Product, Detailed Product, Month, Importer, Date, Origin Country, Customs, Transport, Departure Country, FOB USD, FOB Unit USD, CIF USD, CIF Unit USD, KG Net, KG Gross, Detailed Product Spanish, Detailed Product Chinese, Year, etc. You may communicate with buyers(importers) directly as per your requirements.
Venezuela customs export Data cover ImpExp, 10-digit HS Code, Product, Detailed Product, Month, Exporter, Date, Destination Country, Destination Port, Customs, Transport, FOB USD, FOB Unit USD, FOB Bolivar, FOB Unit Bolivar, KG Net, KG Gross, Detailed Product Spanish, Detailed Product Chinese, Year, etc. You may communicate with suppliers(exporters) directly as per your requirements.
Venezuela customs Data (VECD) is essential to grow International business. VECD reveal the trading activities of importers and exporters, and give you an unprecedented understanding of the import-export business. Venezuela customs Data (VECD) sample can be viewed and searched on the BTDaaS comtrade system.
 Profiles of Venezuela Statistics Data(VESD)
Profiles of Venezuela Statistics Data(VESD)
Venezuela Statistics Data(VESD) is provided according to the-first-6- digit HS Code. We provide actual live Venezuela Statistics Data(VESD) since 2000 onwards.
Venezuela Statistics Import Data include ImpExp, 10-digit HS Code, Product, Month, Net Weight, CIF Value Bolivares, CIF Value US$, Origin Country, Customs, Transport Method, Procedence Country, Acquisition Country, Gross Weight, FOB Value US$, FOB Value Bolivares, Freight Value Bolivares, Insurance Value Bolivares],Vinculation Type, Commercial Level, HS6, HS4, HS2, Year, etc.. Venezuela Statistics Import Data is useful when you want to check Import Market size of Venezuela.
Venezuela Statistics Export Data include ImpExp, 10-digit HS Code, Product, Month, Net Weight, FOB Value US$, Unit Value FOB US$, Destination Country, Customs, Transport Method, Flag, Gross Weight, FOB Value Bolivares, Operation Type, HS4, HS2, Year, etc.. Venezuela Statistics Export Data is useful when you want to check export Market size of Venezuela.
Venezuela Statistics import and export Data sample can be viewed and searched on the BTDaaS comtrade system.
 Service Process:
Service Process:
1) Please search the data sample according to your requirement on our website, and confirm if it is what you are interested; If yes, please send the information you require, including the-first-6- digit HS Code, periods you order, and trade type ( import, export, or import & export); It is best for you to download the order form, and please send it to us after filling in. Venezuela HS Code can be searched on the BTDaaS comtrade system.
2) We both sides agree on price and service content; We send you invoice, and then you pay according to the payment route in the invoice; It is best for you to send the remittance copy to us via fax or email;
3) We send you past data in 1 workday, and send the last-month data at the end of every future month via email; You can also view and download the data and report automatically generated in our online system by your user ID and password.
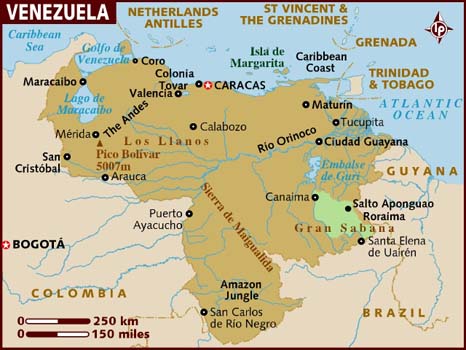
Local Name: Venezuela; Formal Name: Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela
Location: South America
Capital City: Caracas
Main Cities: Maracaibo, Barquisimeto, Valencia
Population: 21,051,000
Area: 912,050 km2
Currency: 1 bolívar = 100 céntimos
Languages: Spanish
Religions: Roman Catholic
 Uzbekistan
Other Asia Countries
Uzbekistan
Other Asia Countries
 China Data
China Data

